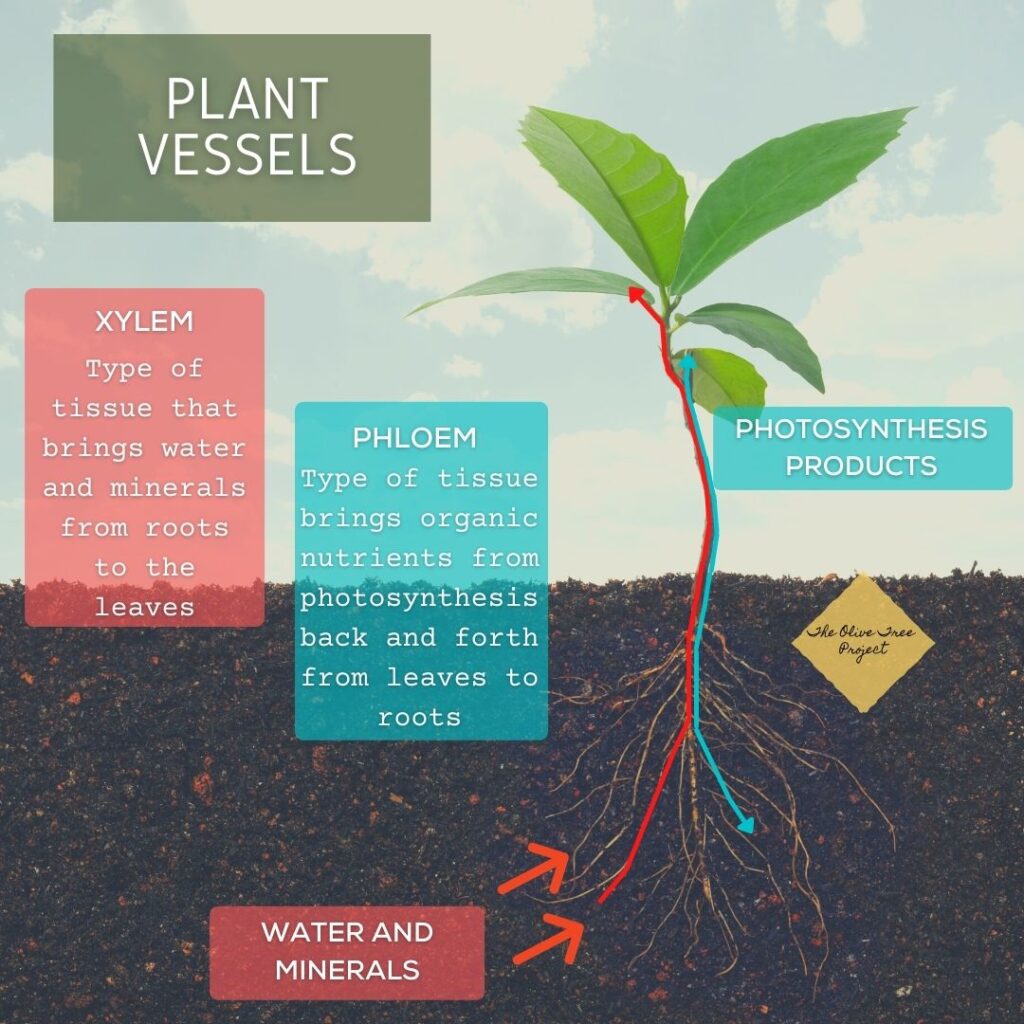
The Xylella Fastidiosa bacteria prevents the host plant from absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. Once infected the plant tissues (called Xylem) that transport hydration and minerals to the leaves, stop working. This causes the plant to dry out and die.
Spreading Via Spittlebug
Plants become infected through a common field insect that nourishes itself from the plants’ Xylem. Xylems are straw like tubes and act as the plant’s veins. Xylems are tissues that bring the minerals and water from the roots to the leaves. There are various insects that feed from the Xylem and drink the Xylem fluid.
In Puglia, the Spittlebug is the main culprit for the spread of the Xylella Fastidiosa bacteria. They are the vectors for the infection. When drinking the Xylem fluid from a contaminated tree, they become an intermediary host and can transfer the bacterium to the next tree or plant the insect decides to feed on.
Spittlebugs have three stages of life: eggs, nymphs and adults. They jump or fly from plant to plant feed during most of their lives, which lasts a little less than a year. Spittlebugs are actually what the insect is called during it’s nymph stage. When they become adults they become known as froghoppers. These insects are known for their mouthparts that are specialized for piercing and sucking. The spittlebug has strong pumping muscles as it’s able to pull the fluid away from the root, against gravity.
For Interesting facts about the spittlebug, click here.
Spreading Via Globalization
Another cause for the spread across continents is globalization. As it becomes easier for people and goods to travel long distances, it also becomes easier for the transfer of the XF bacterium. XF can infect over 595 plant species and not all show symptoms. Buying a plant online from another country or travelling with a plant runs the risk exposing plants to pathogens not native to the continent. XF was first found in the Americas and through globalization it travelled across oceans to different continents.
To find out which continents have been affected by XF, click here.
To find out which countries in Europe have been affected by XF, click here.
Slowing The Spread Of XF
As the scientists try to contain the spread of XF in Puglia, one of the crucial strategies is through the spittlebug. Clearing overgrowth in the olive groves, spraying Insecticides and using tech that disorients the spittlebugs’ communication are techniques that are being used. Although it hasn’t stopped the spread, it has greatly reduced in rate. In the fall of 2021 scientists have confirmed that the spread rate is 2km a year.
Sources: John Innes Centre in plant and microbial science, ThoughtCo article by Debbie Hadley, University of California Agriculture & Natural Resources, Science Facts, Study: Spittlebugs as vectors of Xylella fastidiosa in olive orchards in Italy, CORNARA Daniele, 2016.
Sign up and stay informed!








